Here you will find selection of successfully defended representative theses from previous years. The current assignment can be found by logging into the HUB platform at this link.
Selected Bachelor’s theses
Automatic Detection of Metastases in Whole-Slide Lymph Node Images Using Deep Neural Networks
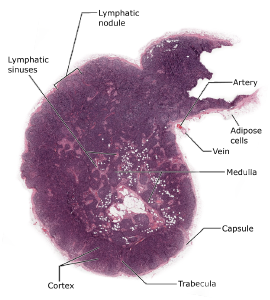
Author: Pavlína Koutecká, 2020
Supervisor: Jan Kybic
Digitisation of cancer recognition in histopathological images is researched topic in recent years, and automated computerised analysis based on deep neural networks has shown potential advantages as a diagnostic strategy. In this thesis, we develop a method for solving the task of automatic metastases detection in whole-slide lymph node images.
Description of epileptic network using distribution of interictal discharges
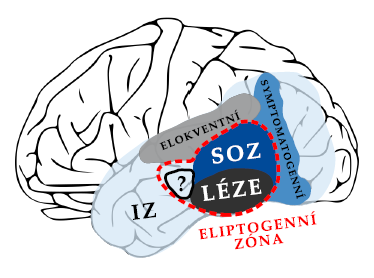
Author: Julie Barnová, 2020
Supervisor: Radek Janča
The irritative zone is a part of the concept of epileptic networks. It consists of subnetworks called clusters which can generate independent populations of interictal epileptiform discharges (IED). The aim of this thesis was to create and optimize an algorithm that would be able to identify independent sources of IED in intracranial EEG (iEEG) as well as demonstrate the relationship between their surgical removal and postoperative seizure freedom.
Assessment of hypometabolism in positron emission tomography
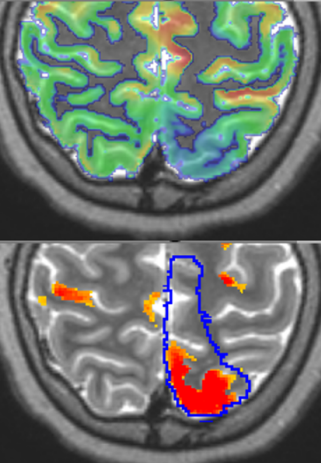
Author: Kateřina Macková, 2021
Supervisor: Radek Janča
For successful surgical treatment of epilepsy, the correct definition of the resection area is crucial. This ideally includes the entire epileptogenic tissue responsible responsible for the onset of seizures. In FDG-PET images, it often appears hypometabolic. Therefore, automatic localization of hypometabolisms can significantly aid in the diagnosis and treatment of focal epileptic seizures.
Selected Diploma theses
Characterization of Photovoltage of Si-V Optical Centers in Diamond Thin Films

Author: Maxmilian Marek, 2024
Supervisor: Bohuslav Rezek
SiV (silicon-vacancy) centers are optically active defects in the diamond matrix that have unique properties of high photostability, biocompatibility and are also inert. The use of SiV centers is currently being intensively developed for a wide range of applications, from so-called energy harvesting, to biomedicine, to applications in quantum information technology. This work investigates the principle of surface photovoltage generation caused by the presence of SiV centers in a nanocrystalline diamond layer with different surface finish and thickness (6-177 nm).
Firmware for Medical Therapeutic Laser Scanner

Author: Matyáš Pokorný, 2024
Supervisor: Tomáš Radil (BTL)
This thesis deals with the design and development of software for controlling the galvanometers of a laser scanner being developed for use in aesthetic medicine. In the introduction, the technology of galvanometer actuators and their control methods are described. Furthermore, the issues of software development for medical devices according to the IEC 62304 standard are briefly described. Based on a mathematical model of galvanometer and simulations, a digital controller for controlling galvanometers is proposed. The controller has the structure of a modified PID controller. The proposed solution is then implemented for STM32 microcontroller and tested using oscilloscope.
Pupil Size Changes in Stress and Anxiety

Author: Tereza Baštová, 2024
Supervisor: Roman Čmejla
The use of physiological signals to measure stress offers some advantages over self-assessment-based methods (e.g., questionnaires), which are highly subjective and may not reliably detect stress symptoms. Commonly used physiological signals for stress detection include pupil size, galvanic skin response (GSR) and heart rate variability (HRV). The aim of this study was to design an experiment suitable for pupillometric measurements, analyze the data obtained and determine the parameters suitable for stress detection.
Classification of Realisations of Random Sets

Author: Bogdan Radović, 2024
Supervisor: Kateřina Helisová
Random sets have gained significant importance in recent years as a valuable tool for modelling a wide range of phenomena in fields such as biology, geology, medicine, or material sciences. However, to the best of our knowledge, classification of their realisations has not yet been studied. In the presented work, a link between methods for random sets and functional data analysis is built that focusses on evaluating functional characteristics from individual components in the realisations based on their shape. Such obtained functional data is then used for nonparametric classification using both supervised and unsupervised approach based on k-nearest neighbours and k-means algorithms, respectively.
Automatic Classification of Social Interactions of Rats from Video

Author: Fádi Kanout, 2024
Supervisor: David Levčík (FÚ AV ČR)
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia. Social behavioural impairment is often an early symptom of AD, typically appearing before the onset of cognitive impairment. The main goal of this work is to develop algorithms for automatic detection and classification of different types of specific social interactions in TgF344-AD rats, an animal model of AD. The rats were observed using cameras from multiple angles, which allowed tracking the movement of the rats in a three-dimensional coordinate system.
Neural Coding of Social Memory in the TgF344-AD Transgenic Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease

Author: Jan Touš, 2024
Supervisor: David Levčík (FÚ AV ČR)
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in the elderly population and places an extraordinary burden on the healthcare system. Disruption of social behaviour is one of the typical early symptoms of AD. The main goal of this work is to develop tools for the identification and analysis of specific patterns in intrusive EEG in rats, specifically a sharp wave and spike detector, tools for quantifying the energy of frequency bands in intrusive EEG recordings, and tools for quantifying the inter-frequency coupling of invasive EEG recordings.

Author: Carmen-Anna Konicarová, 2024
Supervisor: Eduard Bakštein
Previous studies have shown a relationship between actigraphy-measured activities (activity level, sleep and their fragmentation) and clinical status in patients with bipolar disorder. The main aim of this study was to determine whether the structure of the covariance between different actigraphy parameters differs in different clinical conditions. Methods based on the covariance matrix, median and standard deviation of actigraphy trait values were combined with two dimensionality reduction techniques, principal component analysis and our own method based on the maximum difference of covariance pairs of traits between clinical conditions.
Automatic Determination of Knosp Score Based on Segmentation of Anatomical Structures

Author: Filip Oplt, 2024
Supervisor: Martin Černý
This work deals with the automatic determination of Knosp scores from brain MRI images and their segmentation masks. The Knosp score is a grade on the scale of the expanded classification system for assessing the severity of pituitary adenoma. Determination of this score may help to stratify the risks of neurosurgical treatment. The presented solution includes a rule-based geometric model and models using deep learning methods.
Language Analysis of Patients with Schizophrenia

Author: Karolína Bendová, 2024
Supervisor: Roman Čmejla
Schizophrenia is a psychotic disorder whose main symptoms include speech disorders. It affects about 1% of the population. Successful treatment is greatly helped by correct and early diagnosis. The aim of this paper is to propose and test potential language biomarkers that could enable early diagnosis.
Surgery planning using branch-and-price algorithm accelerated using machine learning

Author: Pavlína Koutecká, 2023
Supervisor: Přemysl Šůcha
The planning of operating theatres in healthcare facilities is a crucial task affecting the quality of patient care and operating costs. Scheduling rules used in hospitals often lead to suboptimal schedules. Optimization techniques offer a promising starting point. However, solving the operating room scheduling problem is difficult due to the large number of variables and constraints. This paper solves this problem by using a branch-and-price algorithm.
Optimizing an EIT-Oxygenator Inferface for Early Blood Clot Detection

Author: Filip Šlapal, 2023
Supervisor: Jan Havlík
The formation and deposition of thrombi is the most common cause for forced exchange of oxygenators during extracorporeal circulatory support. However, the incidence of complications is much higher in the case of forced exchange than in the case of planned exchange. This thesis focuses on the use of electrical impedance tomography (EIT) for early detection of blood clots in oxygenators.
Localization and segmentation of in-vivo ultrasound carotid artery images
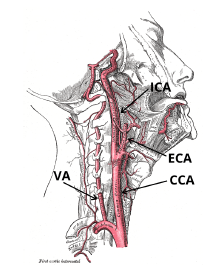
Author: Martin Kostelanský, 2021
Supervisor: Jan Kybic
This thesis is focused on the three separate image recognition tasks—classification, localization, and segmentation of the ultrasound images of the carotid artery with stenosis. The first problem was successfully solved by a ResNet50 CNN and a created dataset with 1,679 images.
Subtype Classification of Focal Cortical Dysplasia by Interictal Activity of Invasive EEG
Author: Laura Shala, 2020
Supervisor: Radek Janča
Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) is a frequent cause of drug-resistant epilepsy. Determining the FCD subtype is essential in planning resection surgery in those patients. The aim of this work is to predict the FCD subtype based on the parameterization of the occurrence of interictal discharges IEDs in the preoperative iEEG recording.
Effective Connectivity Instability within Epileptogenic Network
Author: Lenka Svobodová, 2019
Supervisor: Radek Janča
One of the treatment options for pharmacoresistant epipsy is surgical removal of the epileptogenic zone. In the epileptogenic neural network we can identify nodes that are actively involved in the seizure genesis. These nodes show unstable effective connectivity with the rest of the network. The aim of this work is to identify unstable hubs, their localization in relation to clinical evaluation and the effect on surgical outcome.
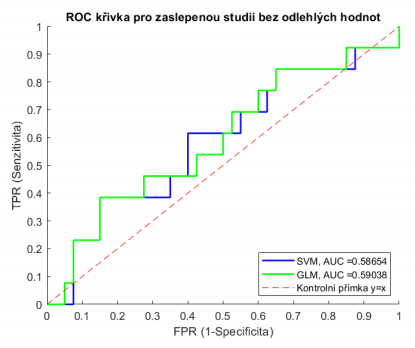
Author: Kristýna Vieweghová, 2021
Supervisor: Radek Janča
This diploma thesis focuses on the statistical analysis of patient’s data after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). The main aim is to find predictors of the post-operative atrial fibrillation using multivariate statistical models. Theoretical part summarizes information about heart conduction system, evaluation of EKG and analysis of heart rate variability.
Secondary structure search in primary nucleic acid structures
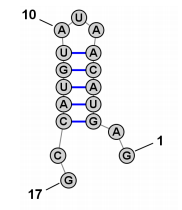
Autor: Anh Vu Le, 2019
Vedoucí: Jiří Kléma
Structure of RNA molecules is often important for their function and regulation. Discovering a particular functional structure within a genome could then be viewed as discovering the associated function. This work proposes a computational pipeline, that searches the human genome and outputs potential IRES candidates
Neural Network Cascades to Incorporate Domain Knowledge for Hematopoietic Cell Classification
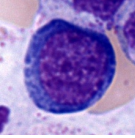
Autor: Jonas Daniel Nienhaus, 2020
Vedoucí: Philipp Gräbel, Jan Havlík
In this work, classification of haematopoietic cells is performed hierarchically, employing cascades of deep neural networks. Two strategies are defined to obtain combined predictions from the cascades, a probabilistic approach and a greedy, deterministic method.
Automatic intron detection in metagenomes using neural networks.
Autor: Martin Indra, 2021
Vedoucí: Jiří Kléma
Exact biological mechanisms of intron recognition and splicing are not fully known yet and their automated detection has remained unresolved. Detection and removal of introns from DNA sequences is important, e.g., for the identification of genes in metagenomes. Two neural network models were developed as part of this thesis. The models’ aim is the detection of intron starts and ends with the so-called donor and acceptor splice sites. The splice sites are later combined into candidate introns which are further filtered by a simple score-based overlap resolving algorithm.
